Gateway Metering Bus Balance Management System
-

Field of Application
Electricity
-

Solution Overview
With the advancement of national power market reforms, the scale of power market transactions is continuously expanding. The pilot program for the spot market is being accelerated, the medium- and long-term power trading mechanisms are being continuously improved, and the market-based mechanisms for the consumption of clean energy are becoming increasingly diversified. Inter-provincial transactions, intra-provincial transactions, medium- and long-term transactions, and spot transactions are more efficiently coordinated and connected. In order to improve the lean management level of electricity metering at power plants, substations and other gateways of provincial and municipal power companies, a power company has launched the construction of a cross-provincial gateway metering bus balance management system.
The system utilizes Internet of Things (IoT) technology to achieve minute-level high-frequency data collection from the power grid. It integrates various data through technologies such as big data platforms, data exchange platforms, and microservices, enabling multi-dimensional data fusion, massive data statistics, and cross-system analysis. The system employs SVG graphics to provide visual monitoring of gateway metering, displaying the operational status of each plant and substation in real time, and offering convenient access to plant/substation equipment and data information at any time. -
Solution Highlights
1. Building multi-channel communication technology based on asynchronous interaction technology to achieve high-concurrency collection and verification of massive data
The system technically achieves minute-level collection of 22 operational data items from power meters at substations/gateways. It employs distributed task scheduling and business collaboration methods for real-time electricity amount data collection and verification, ensuring data timeliness and accuracy. Through high-speed data transmission, the electricity amount data is delivered to various data analysis layers for modeling and visualization, thereby better supporting user business operations.
Figure 1 - System Hierarchical Data Business Architecture Diagram
2. Constructing equipment abnormality diagnosis models through multi-level data integration to achieve accurate abnormality positioning and closed-loop management
The system provides life-cycle, visualized closed-loop management of various abnormal issues in power plants. It tracks the problem-solving processes, visually displays key nodes, and retains crucial handling information, making the abnormality handling processes visible. This helps users handle various abnormal issues quickly and efficiently, enhancing the timeliness of equipment management.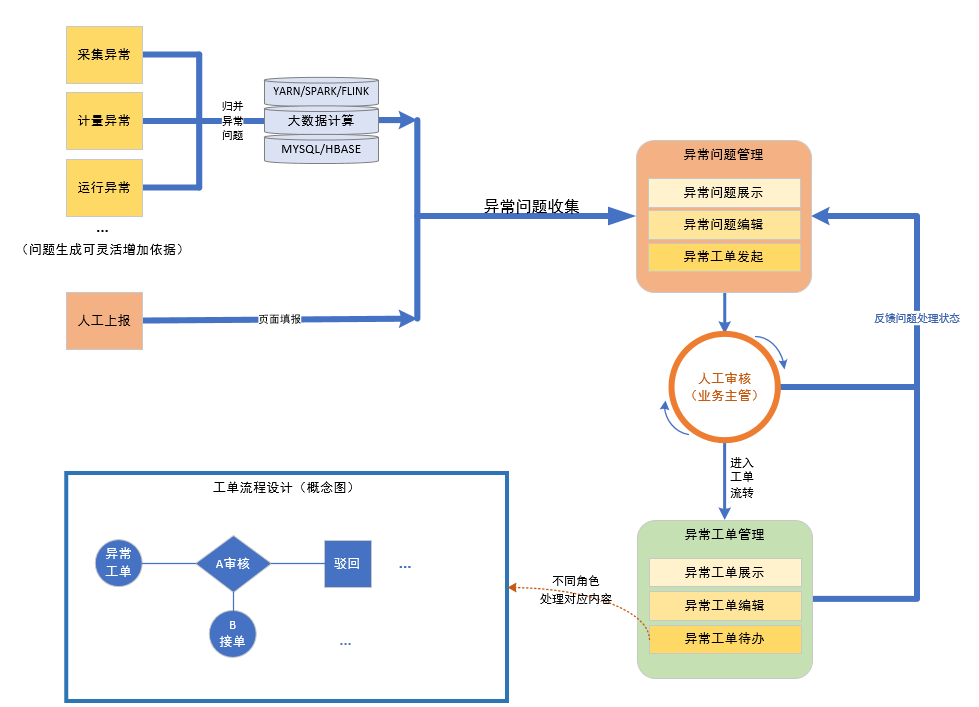
Figure 2 - Abnormality Closed-Loop Management Business Architecture Diagram
3. Using knowledge graphs to build equipment status analysis models and establish a metering device performance evaluation system
The system’s minute-level collection capabilities of electricity amount data and telemetry data supports real-time analysis of massive datasets, meeting the needs of big data applications. The system employs statistical methods combined with expertise in electric power metering to build the algorithm model. This supports the electric power trading center in monitoring, analyzing, and evaluating various operational indicators of metering devices.
Figure 3 - Status Evaluation Module Business Architecture Diagram
4. Integrating real-time data to construct dynamic SVG diagrams to support the visual monitoring system for plant and substation equipment operations and anomalies
Based on the primary wiring diagrams of the plants and substations, the system visualizes internal plant circuits, enabling model visualization capabilities. By covering all metering points at the plants and substations, the system achieves real-time monitoring, timely warning, and visual tracking of plant/substation equipment operations and overall electrical power imbalance, further improving the lean management level of metering operations.
Figure 4 - Visual Management Module Business Architecture Diagram
-

Solution Architecture
Presents the business process architecture in a hierarchical way
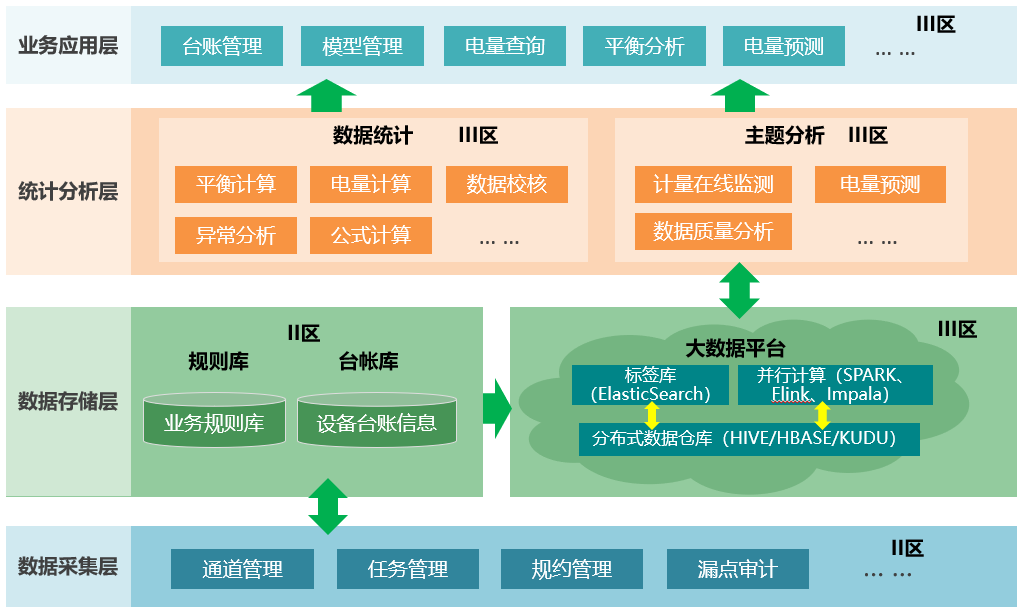
Figure 5 - System Business Architecture Diagram

Figure 6 - Data Analysis Flowchart
-

Success Stories
A Power Company’s Gateway Metering Bus Balance Management System Transformation
A Power Company’s Gateway Metering Bus Balance System Promotion and Main Substation Advanced Application Upgrading
A Power Company’s Technical Transformation of Gateway Metering Devices and Auxiliary Equipment for Supporting the Inter-Provincial Spot Markets






